What is a virtual private cloud (VPC)?
A virtual private cloud (VPC) is a solid, disconnected private cloud facilitated inside a public cloud. VPC clients can run code, store information, have sites, and do anything more they could do in a conventional private cloud, however, the private cloud is facilitated from a distance by a public cloud supplier. (Not all private clouds are facilitated in this style.) VPCs join the adaptability and comfort of public cloud registering with the information detachment of private cloud processing.
What is a public cloud? What is a private cloud?
A public cloud is a shared cloud framework. Multiple clients of the cloud seller access that equivalent foundation, despite the fact that their information isn't shared - very much like each individual in a café order from a similar kitchen, however, they get various dishes. Public cloud specialist co-ops incorporate AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Sky Blue, among others.
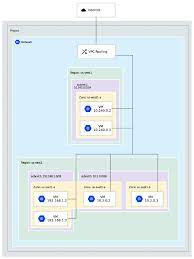
Understand VPC Network with example
How is a VPC segregated inside a public cloud?
A VPC confines registering assets from the other processing assets accessible in the public cloud. The critical innovations for disengaging a VPC from the remainder of the public cloud are:
Subnets
A subnet is a scope of IP addresses inside a network that are saved so that they're not accessible to everybody inside the network, basically separating parts of the network for private use. In a VPC these are private IP addresses that are not open through the public Web, dissimilar to commonplace IP addresses, which are freely noticeable.
For more information about “VPC Network” click here
A VPC will have a committed subnet and VLAN that are just opened by the VPC client. This forestalls any other individual inside the public cloud from getting to figuring assets inside the VPC - actually putting the "Held" sign on the table. The VPC client associates through VPN to their VPC, with the goal that information passing into and out of the VPC isn't noticeable to other public cloud clients.
Some VPC suppliers offer extra customization with:
Network Address Interpretation (NAT): This component matches private IP addresses to a public IP addresses for connections with the public Web. With NAT, a public-confronting site or application could run in a VPC.
BGP course setup: A few suppliers permit clients to modify BGP steering tables for interfacing their VPC with their other foundations. (Figure out how BGP functions.)
What are the upsides of utilizing a VPC rather than a private cloud?
Better performance: Cloud-facilitated sites and applications commonly perform better compared to those facilitated on nearby on-premises servers.
Better security: The public cloud suppliers that offer VPCs frequently have more assets for refreshing and keeping up with the foundation, particularly for little and mid-market organizations.